Schedule Compression
Schedule compression refers to techniques used to shorten the duration of the project without effecting the scope of the project but could have impact on Cost.
Crashing
Most Project Managers have gone through a situation where they receive a project with a challenging schedule to deliver on time. At times, you are told to crash the schedule or just make it happen. Crashing a schedule refers to reducing or shortening the project schedule. Project managers use various techniques to achieve this goal such as:
- Add additional means to the critical path tasks. This option comes with different limitations in securing the budget to add resources.
- Minimize project requirements or scope. Though this is only possible if major stakeholders agree to reduce the scope.
Subsequently applying the crashing, the critical path might be required to get altered or result in developing a different critical path. Therefore, it’s important to thoroughly go through the project schedule and make sure the schedule is crashed. Crashing evaluates critical activities depending on the lowest cash cost per time permitting the team to recognize those applicant activities that would produce the best value at the minimum incremental cost. The result of crashing is typically plotted in a crash graph where practices with the flattest slope would be considered.
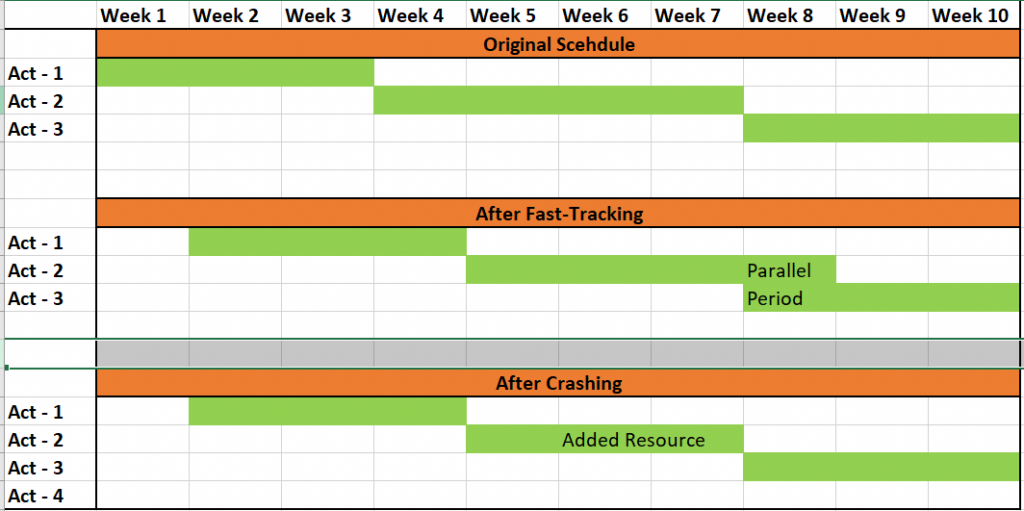
Fast Tracking
In Fast Tracking, you are required to evaluate the critical path and identify which sequential practices can be performed parallel or partially equivalent to one another. It’s important to understand that the purpose of reviewing activities on the critical path is because other paths practices come with floats. There is no need to minimize the duration of those practices since you only need to give those activities more float.
Also, you can start working on the activities to minimize the schedule once you know which one can be fast-tracked. One significant benefit of fast-tracking is that it does not cost any additional money. Nevertheless, it comes with certain risks as you are required to perform many activities in parallel that were initially planned in sequence. The competence to fast track implies that start to finish the relationship between the activities is optional.
On the other hand, crashing is used if fast-tracking is unable to save sufficient time on the schedule. The technique is primarily used when cost and schedule are evaluated to determine how to acquire the greatest amount of compression for the slightest incremental cost. For example, if the present project schedule doesn’t meet the timeline as needed for the project, you may identify that fast-tracking the training material development is required. The training material development begins as the screenshots are produced against waiting for the system to receive final sign-off. This allows the schedule to reduce without incurring extra costs. If the fast-tracking doesn’t speed up the schedule, the project team considers adding resources to the task’s critical activities. As a project manager, you will consider what resources come with the lowest associated costs and begins with the lowest incremental cost resource pool first.
Comparison
- Fast-tracking will increase the risk but should be carefully done.
- Crashing will increase the cost
- Fast-tracking uses the resources assigned on the project, task or phase
- Crashing requires additional resources
- Fast tracking can cause re-work
Usage
- The project is delayed because of
- An unrealistic schedule
- unavailability resources
- Risk occurrence
- Due to force majeure
- External Client/Customer Requirement
- Want to deliver earlier to release the resources
- Changes have impacted the schedule
Note:
There is no reason to fast track or crash any activities that are not on the critical path. Fast-tracking is done first as it doesn’t add any cost on the project. Both of these can only be done on task-driven activities and not effort-driven activities.

