The Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) is a document that links requirements throughout the validation process and project lifecyle. The purpose of the Requirements Traceability Matrix is to ensure that all requirements defined for a system are tested in the test protocols.
It ensures that requirements approved in requirements documentation are
delivered at the end of the project.
Advantages of RTM
- Gives an Overview of ALL the requirements
- Shows how requirements are linked to Test Cases
- Makes sure 100% coverage of requirements
- Easy to prepare
- No special tool is required
Optional Items in RTM
- Business needs, opportunities, goals, and objectives;
- Project objectives;
- Project scope/WBS deliverables;
- Product design;
- Product development;
- Test strategy and test scenarios; and
- High-level requirements or detailed requirements.
You know your requirements are complete when you’ve got a way
to verify each of them once they’re built.
Achieving high-quality requirements necessitates engaging with stakeholders to formulate a traceability matrix. This process requires active involvement beyond the confines of the office setting. For well-defined requirements that are measurable, comprehensive, accurate, and endorsed by project stakeholders, the imperative is to convene with stakeholders. Reading between the lines, establishing a robust feedback mechanism, and cultivating a profound understanding of the business are indispensable components of this endeavour.
Requirements Features: Unambiguous (measurable and testable) ,
Traceable, Complete, Consistent & acceptable to key stakeholders.
Similar to documents such as the Stakeholder Register, Risk Register, and other planning documents, the initial stage involves a broad overview. The subsequent refinement and clarification occur through progressive elaboration, a process that progressively enhances the document’s clarity and precision over time.
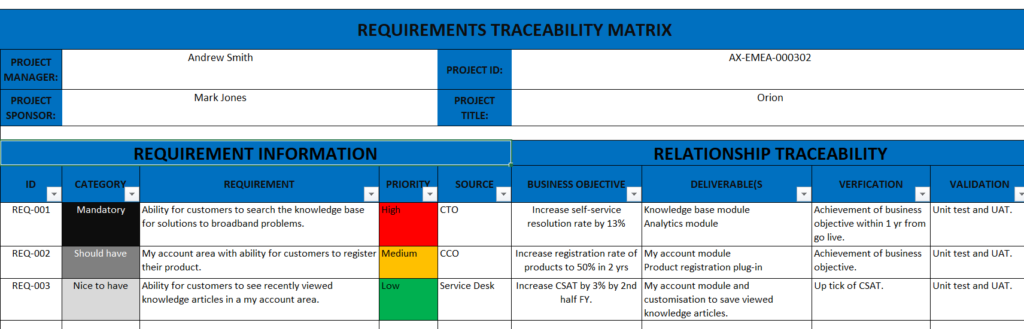
The matrix typically includes:
- Requirement Identifier: A unique identifier is assigned to each requirement for easy reference.
- Requirement Description: A clear and concise description of each requirement to ensure understanding.
- Source of Requirement: Identifies where the requirement originated, whether it came from stakeholders, regulations, or other project documents.
- Status of Requirement: Indicates the current status of each requirement, such as whether it’s approved, in progress, or completed.
- Test Case References: Links to test cases that validate whether the requirement has been satisfied.
- Change History: Tracks any changes made to the requirement over time, including modifications, approvals, or rejections.
Traceability could be Forward traceability, Backward/Reverse or bidirectional.
It establishes a relationship between two artifacts.
And it’s important to be able to trace from one item to the next and back again.
Bidirectional traceability is the ability to trace forward (e.g., from requirement to test case) and backward (e.g., from test case to requirement). That means tracing forward from requirements to source code to test cases to test runs to issues. And from issues back to requirements. You should also be able to trace back from requirements to business goals or objectives (to answer why the requirement is there).
How to Create a RTM
You can create a requirements test matrix (RTM) in Microsoft Excel. Or you can use specialized tools to accelerate the process.
There are three basic steps — no matter which tool you use.
- Define your goals: I want to create a traceability matrix to prove that I’ve met compliance requirements for my product.
- Establish your artifacts (and their relationships) : Requirements, Tests, Test results and Issues
- Fill in the traceability matrix.
The Requirement Traceability Matrix is a valuable tool in project management, helping to ensure that all project requirements are accounted for, understood, and successfully implemented. It facilitates effective communication among project stakeholders and assists in managing changes throughout the project life cycle.
Further Readings
Requirements
Requirements vs Scope
What is a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)?
How to create RTM
Download the template
Traceability Matrix Templates

