The critical path method (CPM) is a project management technique used to plan, schedule, and control a project. It is used to identify the sequence of tasks that must be completed on time in order for the project to be completed on schedule. CPM is a widely used method in many different industries, including construction, manufacturing, and software development. It is a way to visualize the dependencies between tasks and to identify the tasks that have the least amount of slack or buffer time.

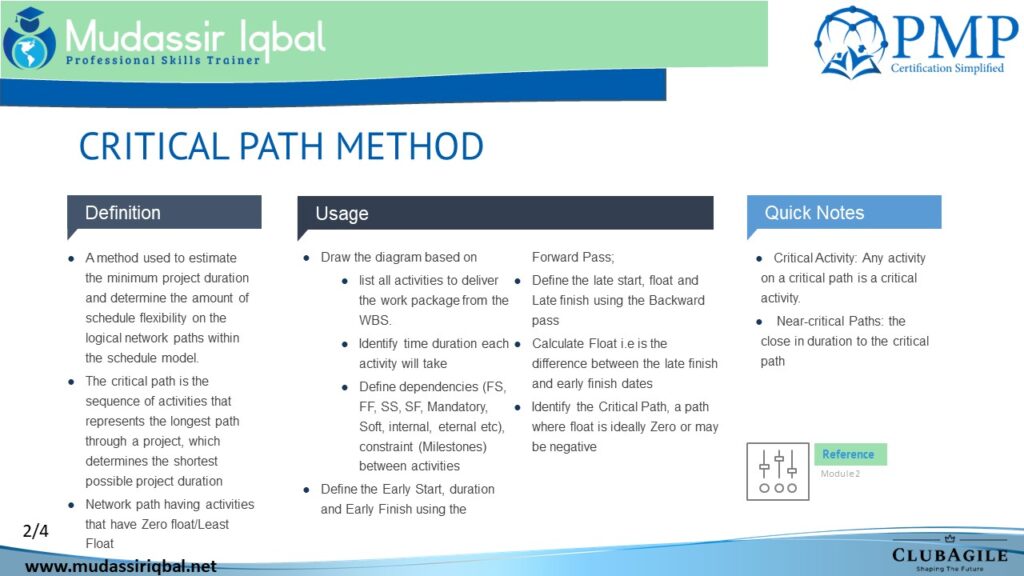
A method used to estimate the minimum project duration and determine the amount of scheduling flexibility on the logical network paths within the schedule model.
Here are the steps to use the critical path method:
- Break down the project into tasks: Identify all the tasks that need to be completed to finish the project.
- Identify the dependencies between tasks: Determine which tasks must be completed before others can begin.
- Determine the duration of each task: Estimate how long each task will take to complete.
- Draw a network diagram: Use a tool such as a Gantt chart or PERT chart to represent the tasks and their dependencies.
- Identify the critical path: The critical path is the sequence of tasks that have zero slack or buffer time. These are the tasks that must be completed on time in order for the project to be completed on schedule.
- Monitor progress: Keep track of the progress of the tasks on the critical path and take action to address any delays or issues
delay in any one of the critical path activities will cause the entire project to be delayed
The schedule network analysis technique calculates the early start, early finish, late start, and late finish dates for all activities without regard for any resource limitations by performing a forward and backward pass
Most critical path analyses are done prior to loading resource availability into the schedule. After resources are loaded, the duration of the project can change, as duration is based on the resources performing the work
It is essential for project managers to identify the critical path because it enables them to:
- Estimate the overall project duration with precision.
- Determine task dependencies, resource limitations, and project dangers.
- Create prioritised and realistic project timelines.
Critical Path Method (CPM) Elements
- Tasks: These are the individual jobs or activities that need to be done in a project. For example, building a house might have tasks like “lay foundation,” “construct walls,” and “install roof.”
- Duration: This is how much time each task takes to complete. It’s like saying, “Task A will take 3 days.”
- Dependencies: Some tasks need to be finished before others can start. For example, you can’t paint a room until the walls are built. These relationships between tasks are called dependencies.
- Earliest Start Time (ES) :The initial stage in the project is when an activity can be begun. You cannot make this decision without initially understanding whether you have any task dependencies.
- Latest Start Time (LS) : The very last second when a task can be started without affecting the timeline for your project.
- Earliest Finish Time (EF): The earliest a task can be finished is determined by its duration and earliest start time.
- Latest Finish Time (LF): The latest that a task can be finished is calculated using its duration and latest start time.
- Float (Slack): Float is the extra time a task can be delayed without affecting the project’s overall timeline. Tasks on the critical path have zero float because any delay would make the project longer.
- Critical Path: This is the sequence of tasks that determines the shortest time to finish the project. If any task on the critical path takes longer, the whole project will be delayed.
- Network Diagram: A visual representation of tasks and their dependencies, usually shown with arrows and nodes. It helps to see the flow of work.
- Forward Pass: Calculating early start and finish times by going forward through the project network, following dependencies.
- Backward Pass: Calculating late start and finish times by going backward through the project network, considering the project end date.
Uses of Critical Path Method
The critical path method is used in project management to identify the sequence of tasks that must be completed on time in order for a project to be completed on schedule. There are several reasons why the critical path method is used:
- Identify critical tasks: By identifying the critical path, project managers can identify the tasks that are critical to the completion of a project and ensure that those tasks are completed on time.
- Visualize dependencies: The critical path method helps to visualize the dependencies between tasks and to identify which tasks must be completed before others can begin.
- Identify slack: The critical path method helps to identify the tasks that have the least amount of slack or buffer time, which can be useful for monitoring progress and taking action to address any delays or issues.
- Improve project planning: The critical path method can help project managers to better plan and schedule the tasks that need to be completed, and to allocate resources more efficiently.
- Better time management: By identifying the critical path, project managers can focus on completing the most important tasks first and avoid wasting time on less important tasks.
- Better communication: The critical path method helps project managers to communicate more effectively with their team and stakeholders by providing a clear and visual representation of the project’s schedule and dependencies.
Definition I – The Critical Path is the longest path to complete the project in the shortest possible duration.
Definition II – Critical Path is the network path having activities that have the least Total Float.
Questions
Q1 – Which of the following is the correct definition of the critical path?
A. The critical path is the fastest path through the network diagram
B. The critical path is the shortest path through the network diagram
C. The critical path is the earliest path through the network diagram
D. The critical path is the longest path through the network diagram*
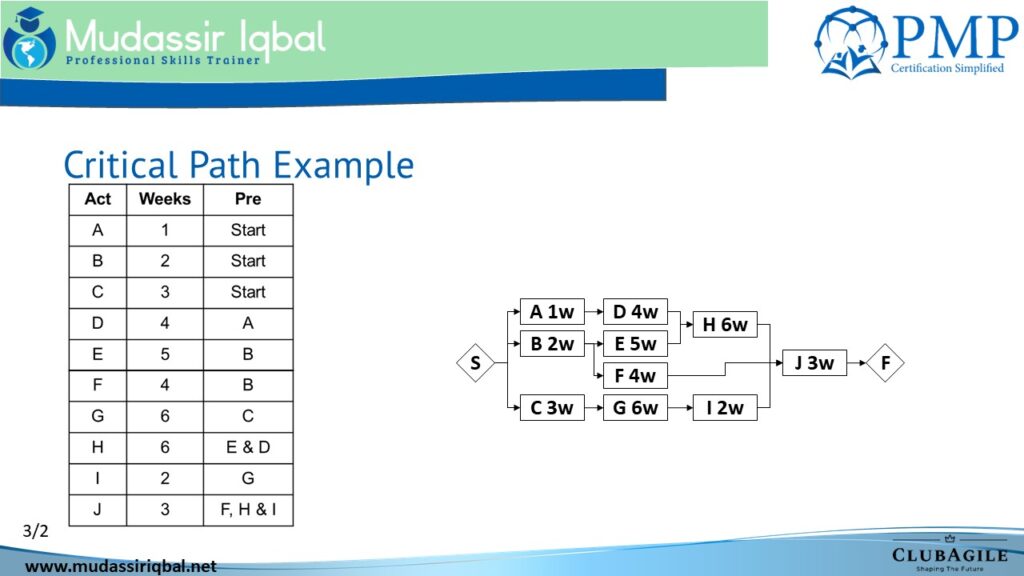
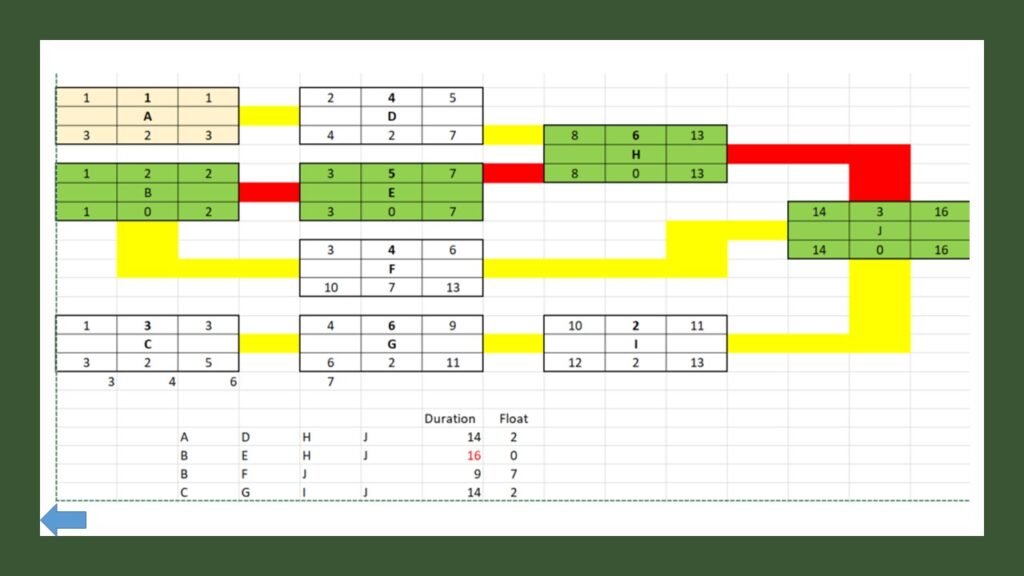
Q2 – What is the duration of the following project?
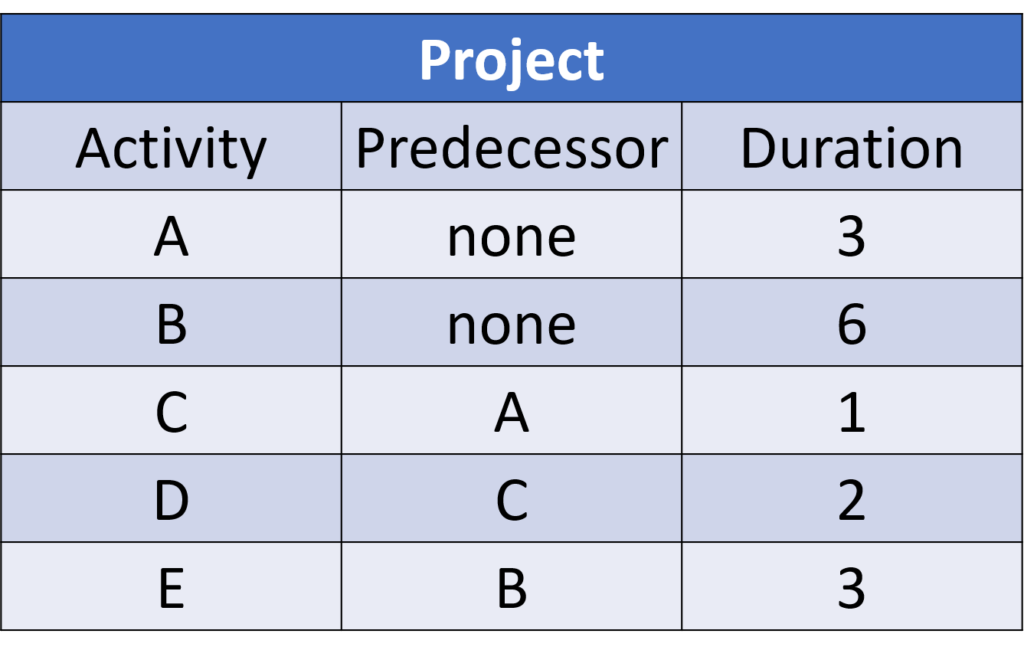
A. 8*
B. 9
C. 7
D. None of the above is correct
Q3 – An activity that comes before a dependent activity in a project schedule is called?
A. Predecessor Activity*
B. Successor Activity
C. Schedule Activity
D. Project Activity
Q4 – In scheduling software Lag is often represented using a negative value
A. False*
B. True


One thought to “Critical Path Method : PMP/CAPM”
Pingback: PRECEDENCE DIAGRAMMING METHOD (PDM) - Mudassir Iqbal