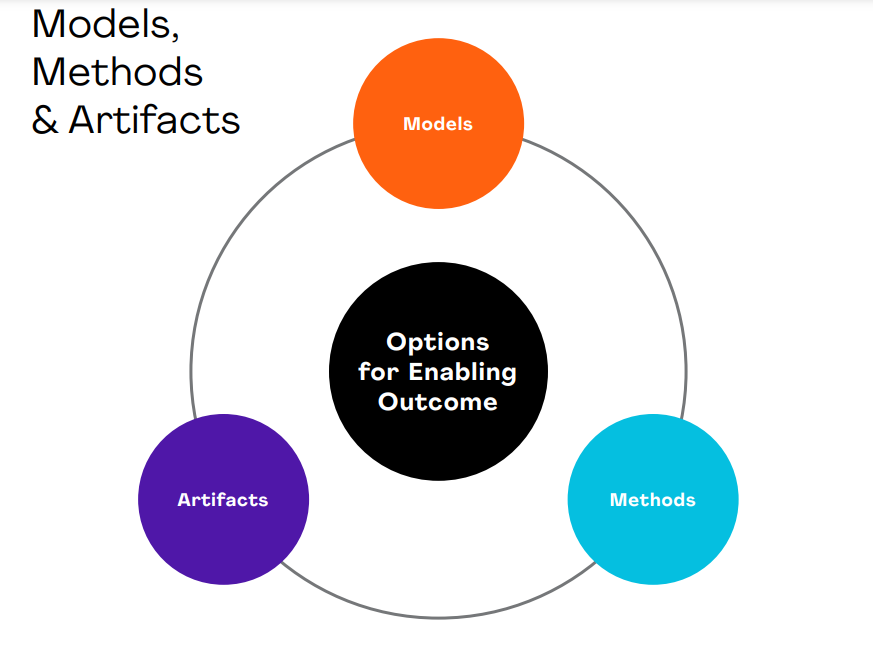
Models, Artifacts and Methods are a set of tools to help you get the Project Management job done. PMi Calls them Options for Enabling Outcome
- Models: A model is a simplified representation of a complex system or process.
- In project management, models can be used to help understand and plan various aspects of a project.
- For example, a project manager might use a risk management model to identify and assess potential risks to the project.
BY PMI Infinity
- Artifacts: Project artifacts are the tangible outputs or deliverables of a project. These can include things like project plans, schedules, budgets, and reports. Artifacts are important because they provide a record of the project’s progress and help ensure that everyone involved in the project is on the same page.
BY PMI Infinity
- Methods: Project management methods are the specific techniques and processes used to plan, execute, and control a project. These can include things like Agile, Waterfall, and Scrum methodologies. Choosing the right method for a project depends on a variety of factors, including the project’s goals, timeline, and budget.
BY PMI Infinity
Models
Models help us to see complex reality as simple, simplified things and show us approaches to optimise our actual work. They help to explain what works in the real world and how it works. These visualizations aid in understanding complex concepts and facilitate effective communication among project stakeholders. e.g Gantt Chart
List Of Models
- Situational Leadership Models:
- Situational Leadership® II
- OSCAR
- Communication Models:
- Cross-cultural communication
- Effectiveness of communication channels
- Gulf of execution and evaluation
- Motivation Models:
- Hygiene and motivation factors
- Intrinsic versus extrinsic motivation
- Theory of needs
- Theory X, Theory Y, and Theory Z
- Change Models:
- Managing Change in Organizations
- ADKAR®
- 8-Step Process for Leading Change
- Transition
- Complexity Models:
- Cynefin framework
- Stacey matrix
- Project Team Development Models:
- Tuckman Ladder
- Drexler/Sibbet Team Performance
- Other Models:
- Conflict
- Negotiation
- Planning
- Process Groups
- Salience
Artifacts
An Artifact can be a template, document, output, or project deliverable. In project management, a project artifact is a document designed to keep the project work aligned with project requirements and business goals. These artifacts provide evidence of project progress, decisions, and outcomes.
For example, a Project Plan is an artifact. It contributes to the overall management of the project work.
Attributes of project artifacts include:
- Created as part of overall project documentation
- Tailored to specifics of the project
- Linked to project management, not project deliverables
- Created by the project manager and project team
- Subject to change as project work progresses
- Referred to as artifacts, documents, deliverables, and/or templates
- Require formal updating
List of Artifacts
- Strategy Artifacts:
- Business case
- Project Brief
- Project charter
- Project vision statement
- Roadmap
- Log and Register Artifacts:
- Assumption log
- Backlog
- Change log
- Issue log
- Lessons learned register
- Risk-adjusted backlog
- Risk register
- Stakeholder register
- Plan Artifacts:
- Change control plan
- Communications management plan
- Cost management plan
- Iteration plan
- Procurement management plan
- Project management plan
- Quality management plan
- Release plan
- Requirements management plan
- Resource management plan
- Risk management plan
- Scope management plan
- Schedule management plan
- Stakeholder engagement plan
- Test plan
- Hierarchy Chart Artifacts:
- Organizational breakdown structure
- Product breakdown structure
- Resource breakdown structure
- Risk breakdown structure
- Work breakdown structure
- Baseline Artifacts:
- Budget
- Milestone schedule
- Performance measurement baseline
- Project schedule
- Scope baseline
- Visual Data and Information Artifacts:
- Affinity diagram
- Burn chart
- Cause-and-effect diagram
- Cycle time chart
- Cumulative flow diagram
- Dashboard
- Flow chart
- Gantt chart
- Histogram
- Information radiator
- Lead time chart
- Prioritization matrix
- Project schedule network diagram
- Requirements traceability matrix
- Responsibility assignment matrix
- Scatter diagram
- S-curve
- Stakeholder engagement assessment matrix
- Story map
- Throughput chart
- Use case
- Value stream map
- Velocity chart
- Report Artifacts:
- Quality report
- Risk report
- Status report
- Agreements and Contracts:
- Fixed-price
- Cost-reimbursable
- Time and materials
- Indefinite time indefinite quantity (IDIQ)
- Other agreements
- Other Artifacts:
- Activity list
- Bid documents
- Metrics
- Project calendars
- Requirements documentation
- Project team charter
- User story
Methods
A method is a means for achieving an outcome, output, result, or project deliverable. The methods described here are a sampling of those commonly used to support project work. It shows the ‘ways’ of doing various things that are usually done within project management, such as data collection, estimation, meetings, etc. A good example would be the Critical Path method
The following is a keyword list of those introduced in the PMBOK,
- Data Gathering and Analysis Methods:
- Alternatives analysis
- Assumptions and constraints analysis
- Benchmarking
- Business justification analysis
- Payback period
- Internal rate of return
- Return on investment
- Net present value
- Cost-benefit ratio
- Check sheet
- Cost of Quality
- Decision tree analysis
- Earned value analysis
- Expected monetary value
- Forecasting
- Influence diagram
- Life cycle assessment
- Make-or-buy analysis
- Probability and impact matrix
- Process analysis
- Regression analysis
- Root cause analysis
- Sensitivity analysis
- Simulation
- Stakeholder analysis
- SWOT analysis
- Trend analysis
- Value stream mapping
- Variance analysis
- What-if scenario analysis
- Estimating Methods:
- Affinity grouping
- Analogous estimating
- Function points
- Multipoint estimating
- Parametric estimating
- Relative estimating
- Single-point estimating
- Story point estimation
- Wideband Delphi
- Meeting and Event Methods:
- Backlog refinement
- Bidder conference
- Change control board
- Daily standup
- Iteration review
- Iteration planning
- Kickoff
- Lessons learned
- Planning
- Project closeout
- Project review
- Release planning
- Retrospective
- Risk review
- Status
- Steering committee
- Other Methods:
- Impact mapping
- Modelling
- Net Promoter Score®
- Prioritization schema
- Timebox
Models, Artifacts, and Methods in Project Management Context
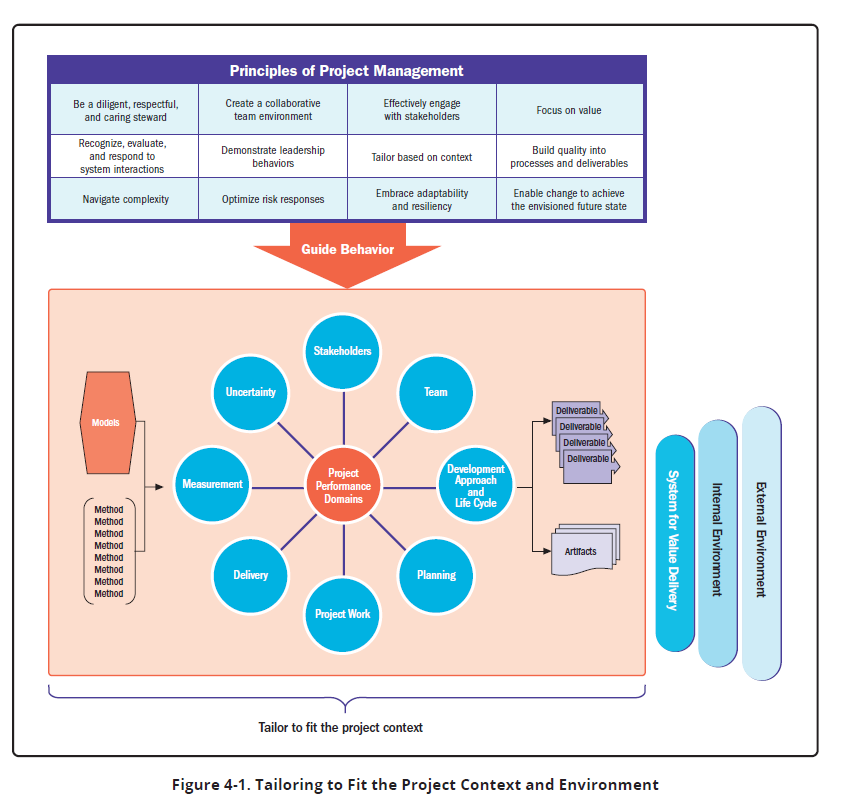
PMP ECO 2021
Domain 2, Task 12 is ‘Manage project artifacts”
- Determine the requirements (what, when, where, who, etc.) for managing the project artifacts
- Validate that the project information is kept up to date (i.e., version control) and accessible to all stakeholders
- Continually assess the effectiveness of the management of the project artifacts
Further Readings
- 8 Project Performance Domains by PMI: The Standard for Project Management – PMBOK 7
- 12 Project Management Principles by PMI: A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge – PMBOK 7
- Types of Project Management Artifacts

